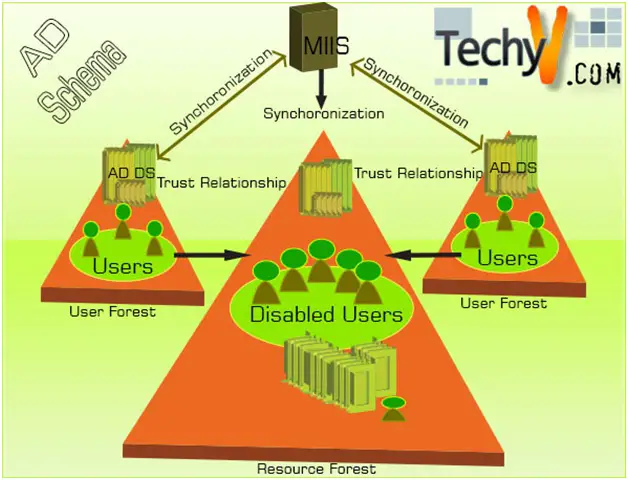
Active Directory Schema
Active Directory is an important management tool used in Windows Server and it offers central authorization in a network. Active Directory provides many directory and network services. Microsoft Active Directory is based on Novell e Directory and it also includes some modified versions of existing protocols that have been updated with time.
Microsoft released Active Directory first time with the release of Windows Server 2000. There has been lot of improvements and upgrades in the Active Directory since the launch. Before moving on the Active Directory Schema, it is important to define the elements that complete Active Directory.
- Domain: The objects in a common directory database are called domain.
- Tree: It consists of single or multiple domains in a contiguous namespace.
- Forest: It is the container that contains the collection of trees, user, groups, computers, and other objects. It is also known as the security boundary of Active Directory.
Active Directory of Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2008 use set of rules for database which are known as Schema. Schema governs database structures and type of objects and attributes that a database contains. Schema is also defined as the formal definition of all object classes and their attributes that can be stored in a directory. Active Directory database includes a default Schema which defines computers, groups, users, domains etc. The Active Directory Schema is dynamic since its attributes can be changed as required in a specific condition since the Schema can be modified according to the requirements. Active Directory Schema can be modified for both the existing objects and new object types.
The objects of Active Directory are stored in Directory Information Tree also known as DIT. Directory Information Tree consists of three partitions; Schema Partition, Configuration Partition and Domain Partition. The Schema Partition defines for the creation and modification of the objects in the forest. Configuration Partition, however, stores information regarding trees, domains, sites and domain trust relationships. Domain Partition has the information regarding all the domain objects such as users, groups etc.
The Schema Partition has a Schema container that contains ‘class Schema’ attributes and ‘attribute Schema’ attributes. Some of the ‘class Schema’ attributes are: default object category, governs ID, NT Security descriptor, object class, sub class Of etc. Further to this, ‘attributeSchema’ attributes are: attribute ID, is single valued, Schema ID GUID etc. It is important to mention that there are some system attributes as well that can only be changed by Directory System Agent also referred as DSA.
The Active Directory Schema contains the rules for the Active Directory database and the modification of Schema should only be performed if necessary. While performing any modifications it is important to test the process before applying it. The Active Directory Schema can be modified by using the below mentioned methods:
- CSVDE bulk Schema updating tool
- LDIFDE bulk Schema modification tool
- LDIF scripts
- Using API
In order to ensure the efficiency of Active Directory and Active Directory Schema, it has a built-in feature of replication. The Schema is replicated in all the Domain controllers as soon as a change is made in it and the replicated data is updated after every modification.